Innovative Warehouse Management with AI
Most popular WMS
Data and AI within WMS world
Conclusion
Warehouse logistics face numerous challenges, including inefficiencies in order fulfillment, inaccuracies in inventory management, and the complexities of supply chain coordination. These issues can lead to increased operational costs, delayed shipments, and unsatisfied customers. However, the integration of advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) offers transformative solutions to these problems, making warehouses more efficient, accurate, and responsive.
TData specialists and AI experts are uniquely positioned to tackle these challenges. By leveraging automation, they can streamline warehouse processes, reducing reliance on manual labor and minimizing errors. This leads to faster and more reliable order fulfillment, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Tasks such as real-time tracking of goods, continuous monitoring of vast inventory amounts, demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, and optimization of the flow of goods are just a small subset of data challenges that can be efficiently addressed in this context.
A robust Warehouse Management System (WMS) acts as the central hub for data integration in warehouse operations. As the core data hub, the WMS facilitates better resource management and provides valuable operational insights, driving continuous improvement. Thus, a WMS can be seen as a central point for applying beneficial data and AI strategies and introducing them effectively to the entire warehouse.
In this paper, we introduce the world of warehousing and WMS, provide a comparative analysis of the main WMS systems, and offer an overview of data analytical problems that can be solved within this context.
What is Warehousing and WMS
Why do we need WMS?
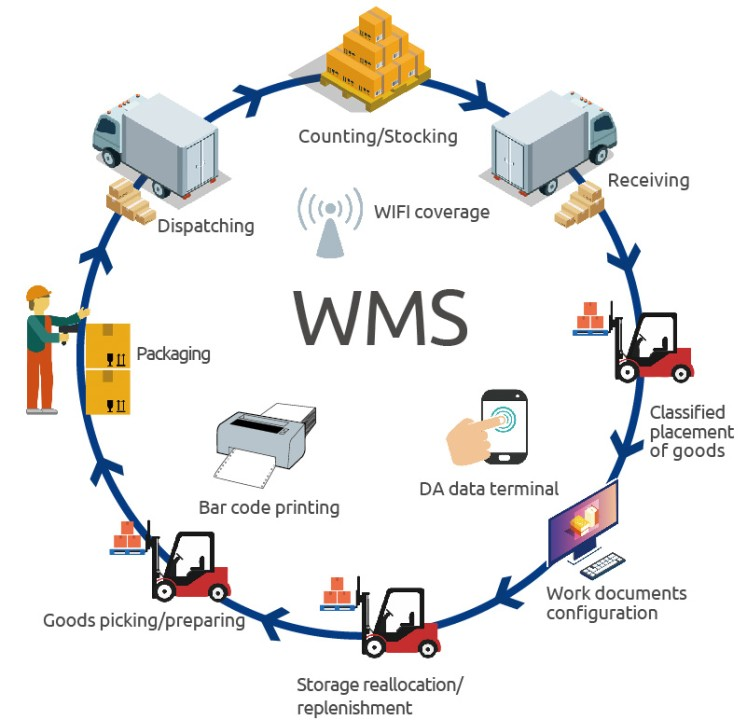
WMS[0]
In today's online retail landscape, efficiently fulfilling orders is crucial. A warehouse management system (WMS) is essential for understanding the location of all materials and goods within a warehouse, which helps reduce order latency, processing costs, and order errors. By providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and movements, a WMS allows businesses to speed up order fulfillment and minimize mistakes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs.
For large enterprises with multiple warehouses in various locations, the complexity of modern logistics and consumer deliveries makes WMS indispensable. These systems are critical for maintaining operational efficiency and profitability by streamlining supply chain operations. Additionally, WMS solutions often integrate with other systems such as e-commerce platforms, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). This integration helps automate and optimize logistics processes from receiving and storage to picking, packing, shipping, and delivery, ensuring a seamless and efficient flow of goods.
Furthermore, a WMS can provide valuable insights into sales trends by tracking which products are selling well. This information allows businesses to optimize warehouse layout, ensuring that best-selling items are positioned near loading docks or packing areas for quicker access. By strategically organizing inventory and monitoring raw materials upon arrival, businesses can enhance stocking and manufacturing processes, ultimately improving overall warehouse efficiency and responsiveness to market demands.[1]
Warehousing
First, let's outline the meaning of warehousing. Warehousing is the process of storing goods until they're ready for transport to retailers, distributors or customers. Serving as temporary storage facilities, warehouses can also function as fulfillment centers and distribution hubs within the supply chain. They facilitate the seamless movement of products from businesses to consumers.
Beyond basic storage, modern warehouses often provide a range of value-added services. These include order fulfillment, packaging, labeling, and kitting. Such services enhance the efficiency of the supply chain by allowing businesses to manage inventory more effectively, streamline the shipment process, reduce distribution costs, and maintain high levels of customer satisfaction.
Warehousing is thus crucial for optimizing logistics and supply chain operations. It ensures that products are available when needed, in the right quantities, and in good condition, thereby supporting the overall efficiency and effectiveness of business operations. Additionally, the strategic use of warehousing can help businesses respond more flexibly to market demands and changes, further contributing to a robust supply chain.[2]
Warehouse Management System (WMS)
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software solution that provides comprehensive visibility into a business's inventory and manages supply chain fulfillment operations from distribution centers to store shelves. It is widely used in manufacturing and retail industries to track materials and goods as they enter, move through, and leave the warehouse. The primary purpose of a WMS is to ensure that these movements are efficient and cost-effective, covering essential functions such as inventory tracking, order picking, receiving, and storage.
In addition to optimizing the movement of goods, a WMS enhances labor and space utilization and maximizes equipment investments. It automates many warehouse processes, reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. Modern WMS solutions also offer value-added services like packaging, labeling, and kitting, which help streamline operations and reduce costs. The system's ability to provide real-time inventory visibility and its support for quick order fulfillment are crucial for meeting the demands of today's dynamic, omnichannel fulfillment economy.[3]
Benefits of using WMS
Here are the key benefits of using WMS in your business:
Increased productivity
Accurate invoice management and inventory records
Lower warehouse costs and operating expenses
Enhanced security
Reducing of “lost” inventory and waste
Better inventory management and traceability
Tracking of materials in real time
Increasing of flexibility
Optimizing of supply chain and warehouse processes
Improving customer and supplier relationships
Scalability as retails business grows
Reducing of human errors
Key functions and processes of WMS
Key functions and processes of WMS include:
Inventory Tracking and Control: Maintains accurate stock levels, manages locations, and offers real-time inventory visibility.
Receiving and Put-away: Enhances the acceptance and storage of goods, reducing errors and increasing storage efficiency.
Order Picking and Packing: Streamlines order fulfillment, minimizes errors, and improves productivity through guided picking lists and various picking methods.
Shipping: Ensures precise and timely deliveries, optimizing order fulfillment and providing real-time tracking.
Labor Management: Monitors and optimizes workforce performance, scheduling, and safety, improving overall efficiency.
Yard Management: Provides control over vehicle and goods movement within the yard, enhancing coordination and efficiency.
Barcode Scanning and RFID Integration: Enables precise and efficient inventory tracking, improving data accuracy and visibility.
Space Optimization: Maximizes storage capacity and optimizes warehouse layout for better efficiency.
Batch and Serial Number Tracking: Ensures precise product tracking and traceability, meeting compliance requirements.
Reporting and Analytics: Delivers insights into warehouse performance, aiding in data-driven decision-making.
Integration Capabilities: Connects seamlessly with other systems like ERP and TMS, enhancing supply chain visibility and control.
Multi-warehouse Management: Centralizes control and oversight across multiple warehouse locations, optimizing inventory management.
Cross-docking: Facilitates efficient transfer of goods from receiving to shipping, reducing storage needs and speeding up order fulfillment.
Returns Management: Streamlines the handling of returned goods, ensuring accurate inventory adjustments and effective processing.
Safety and Security Features: Enhances warehouse safety and security through various protocols and systems.
Mobile Capabilities: Allows warehouse staff to access and update information instantly, increasing productivity and accuracy.[4]
Most popular WMS
With hundreds of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) available on the market, selecting the best one can be challenging. Here, we will focus on the 10 most popular systems and their main pros and cons.
Manhattan Associates WMS
Manhattan Associates WMS is renowned for its highly configurable and scalable solutions designed to handle complex distribution and logistics operations. It offers advanced features such as real-time inventory tracking, labor management, and warehouse automation. The system supports a range of deployment models and is known for its robust integration capabilities with other supply chain systems. This makes it a preferred choice for large enterprises looking to optimize their warehousing efficiency and operational control.
Manhattan Associates WMS[5]
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Blue Yonder - Luminate Logistics (formerly JDA Software)
Blue Yonder's Luminate Logistics, formerly known as JDA Software, leverages AI and machine learning to provide advanced supply chain solutions. The system offers real-time visibility, predictive analytics, and end-to-end supply chain orchestration. It is designed to enhance operational efficiency by optimizing inventory management, labor utilization, and fulfillment processes. Blue Yonder is particularly noted for its ability to adapt to dynamic market conditions and complex logistical requirements.
Blue Yonder - Luminate Logistics[6]
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM)
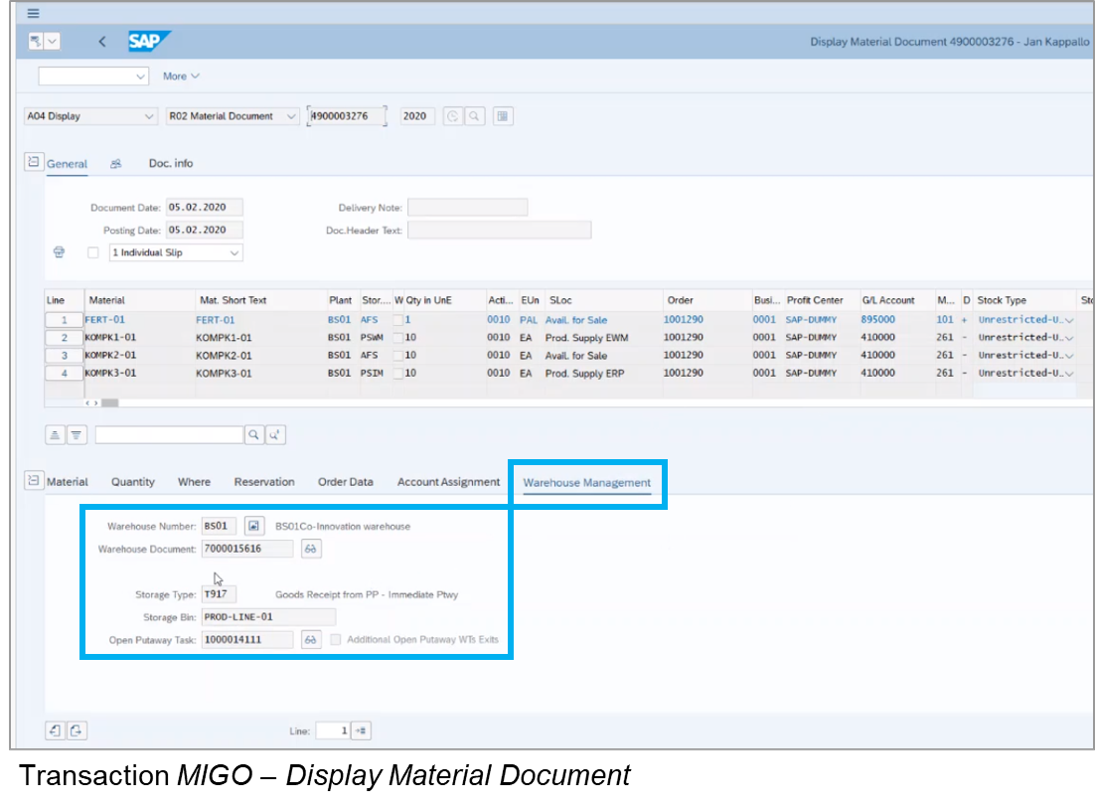
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM)[7]
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) is a robust WMS designed to manage high-volume warehouse operations with precision. It integrates seamlessly with SAP ERP systems, providing real-time data tracking and comprehensive resource management. SAP EWM supports advanced functionalities such as automated picking, packing, and shipping processes, making it ideal for large-scale operations. Its capability to optimize warehouse space and labor utilization ensures efficient and cost-effective warehouse management.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Oracle Cloud WMS
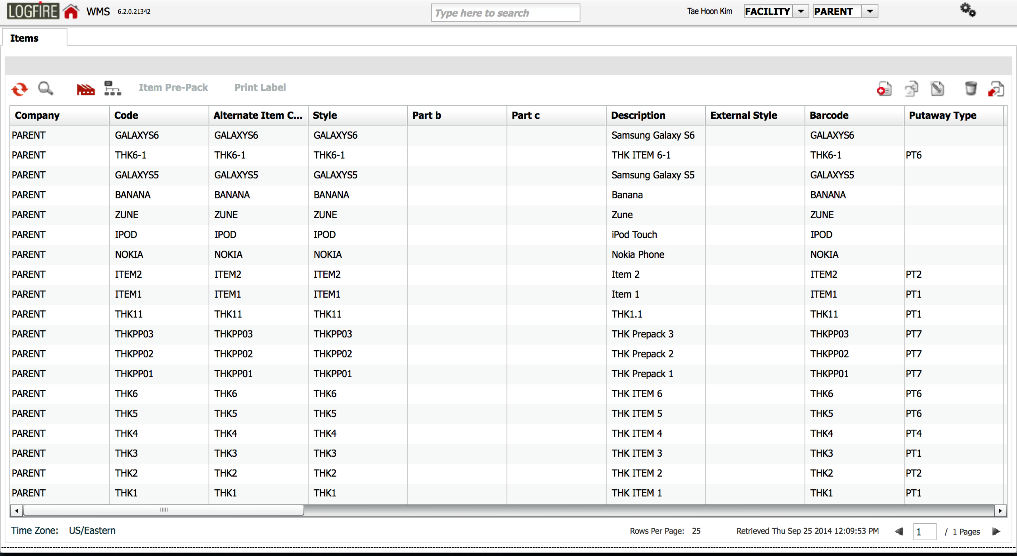
Oracle Cloud WMS[8]
Oracle WMS Cloud is a scalable and flexible WMS solution known for its comprehensive suite of tools that cover inventory, labor management, and warehouse automation. It provides real-time visibility into inventory levels and movements, ensuring efficient order fulfillment and reduced operational costs. The system's robust integration capabilities with other Oracle supply chain solutions make it a preferred choice for enterprises aiming to streamline their logistics processes. Oracle WMS Cloud is suitable for businesses of all sizes, offering the flexibility to scale as needed.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Körber (formerly HighJump)
Körber WMS, previously known as HighJump, is an adaptable warehouse management solution designed to meet diverse warehousing needs. It features a process-based approach and a full HTML5 user interface, supporting both on-premise and cloud deployments. Körber WMS excels in optimizing warehouse operations through advanced inventory management, order fulfillment, and labor tracking. Its ability to integrate with various supply chain systems ensures seamless operational workflows and enhanced efficiency.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
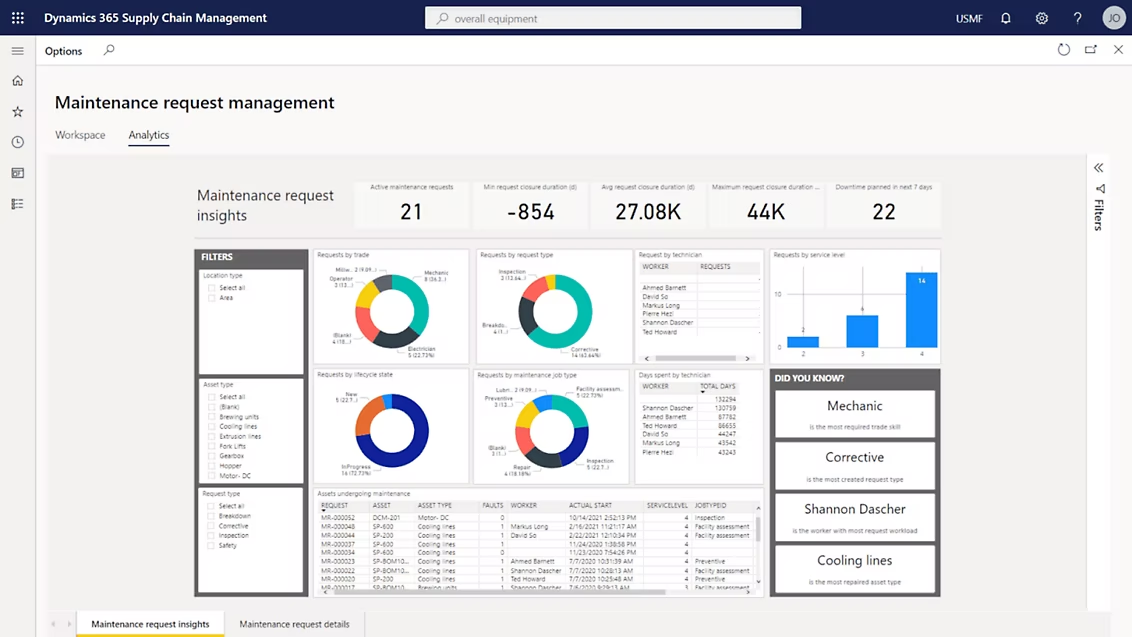
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management[9]
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management offers a comprehensive suite of tools for managing and optimizing supply chain operations, including warehousing. The system provides real-time insights, advanced analytics, and robust integration capabilities with other Microsoft applications. It supports efficient inventory management, order processing, and logistics planning, helping businesses streamline their supply chain activities. Dynamics 365's cloud-based architecture ensures scalability and flexibility for enterprises of all sizes.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Infor SCM WMS
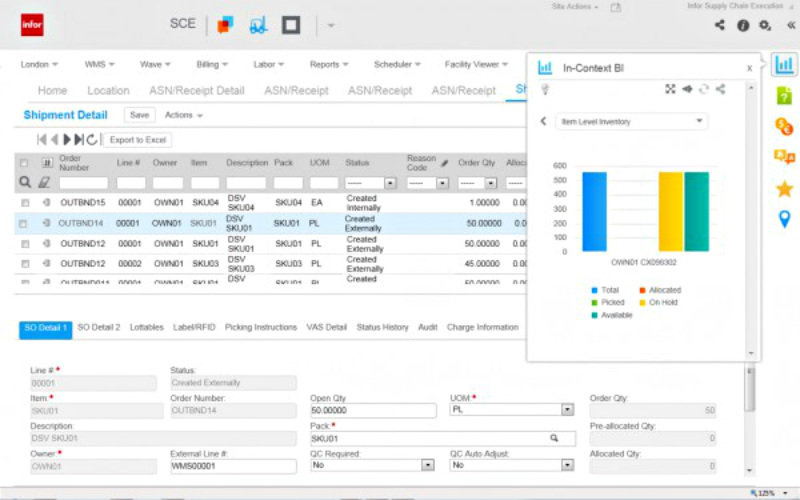
Infor SCM WMS[10]
Infor SCM Warehouse Management is a cloud-based WMS designed to optimize warehousing operations through advanced inventory control, labor management, and order fulfillment features. It offers real-time data visibility, predictive analytics, and seamless integration with other Infor supply chain solutions. The system is known for its user-friendly interface and ability to scale according to business needs. Infor SCM WMS is ideal for enterprises looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce logistics costs.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Softeon WMS
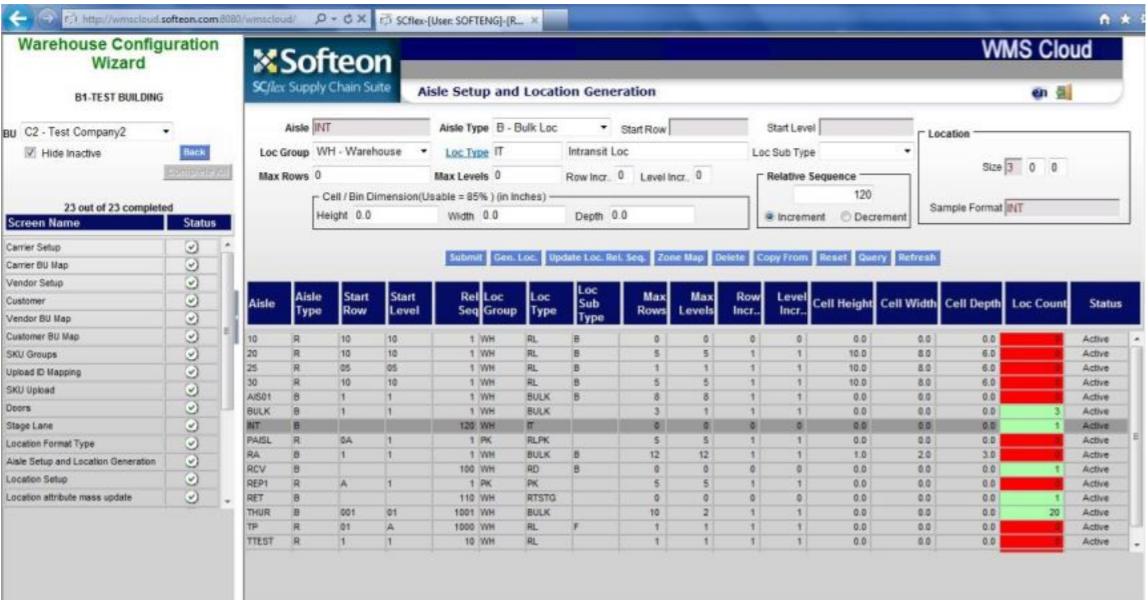
Softeon WMS[11]
Softeon WMS provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing warehouse operations, focusing on flexibility and scalability. The system supports advanced functionalities such as real-time inventory tracking, automated order processing, and efficient labor management. Softeon WMS is designed to integrate seamlessly with other supply chain systems, ensuring streamlined workflows and enhanced operational efficiency. It is suitable for businesses of all sizes, offering customizable solutions to meet specific warehousing needs.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
EPG LFS WMS
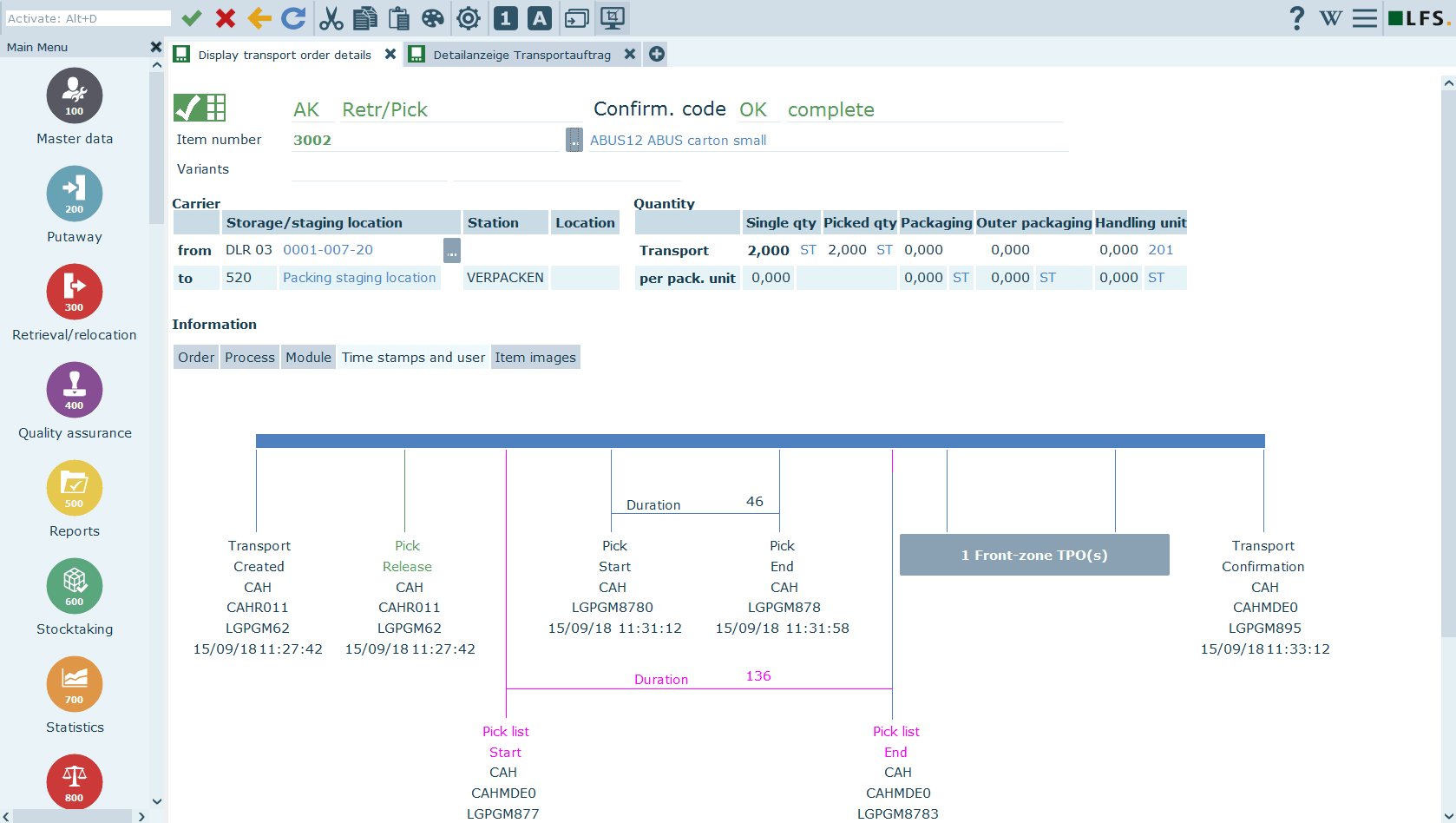
EPG LFS WMS[12]
EPG LFS is a highly adaptable warehouse management system known for its flexibility and extensive functionality. It offers real-time inventory management, advanced order processing, and robust labor management features. The system supports multiple deployment models and integrates seamlessly with various supply chain systems. EPG LFS is designed to optimize warehouse operations, ensuring efficient and cost-effective logistics management.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
LEA Reply
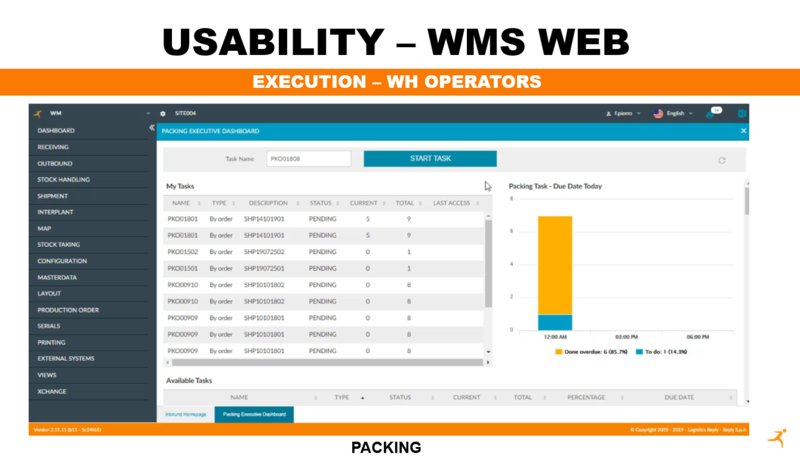
LEA Reply[13]
LEA Reply is a modern WMS designed to enhance warehouse operations through advanced technology and real-time data analytics. The system offers comprehensive tools for inventory management, order fulfillment, and labor optimization. LEA Reply is highly flexible, supporting various deployment options and seamless integration with other supply chain solutions. It is ideal for businesses looking to improve operational efficiency and achieve greater visibility into their warehouse activities.
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
Data and AI within WMS world
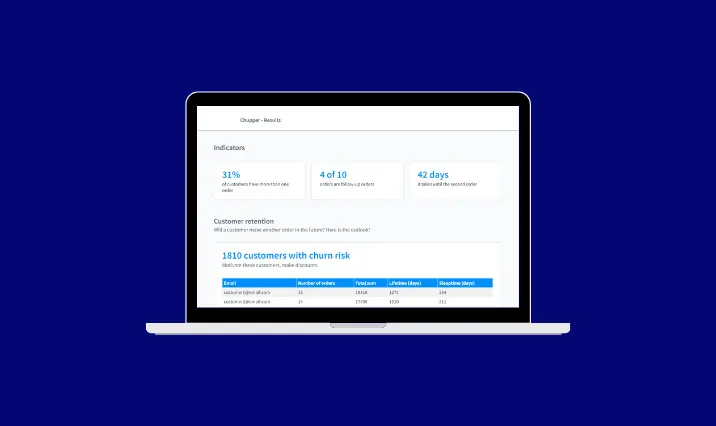
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in modern warehouse management systems (WMS), transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive operational efficiency and strategic decision-making. By leveraging advanced analytics, warehouses can optimize inventory levels, improve order accuracy, and enhance overall supply chain performance. Key areas where data analytics proves invaluable include demand forecasting, inventory replenishment, and throughput analysis. It enables real-time tracking and monitoring of warehouse activities, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies promptly. Furthermore, data analytics supports predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Ultimately, the integration of data analytics into WMS empowers businesses to respond swiftly to market changes, reduce operational costs, and increase customer satisfaction.
Further we will check the key data analytics features in WMS.
Stock/Inventory Planning
Inventory (stock) planning is the process of ensuring that the right amount of stock is available to meet customer demand while minimizing costs. This involves forecasting future demand, considering factors such as sales trends, seasonality, and market conditions. It also includes managing supplier lead times and setting appropriate reorder points to maintain optimal inventory levels. The goal is to avoid stockouts, which can lead to lost sales, and overstocking, which ties up capital and increases storage costs. Effective inventory planning enhances operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall profitability.[14]
Inventory/Stock Replenishment
Inventory replenishment, also known as stock replenishment, involves models, practices, and technologies to efficiently manage the movement of stock from a central location to downstream locations. It ensures the smooth flow of inventory from reserve to primary storage and from there to picking locations.
Goals of Inventory Replenishment
Avoid excessive overstock and reduce carrying/storage costs
Ensure on-time deliveries
Minimize labor costs
Cut back on dead stock and slow-moving items
Reduce the risk of logistical problems
Improve replenishment planning
Meet demand without shortages
Maintain adequate safety/buffer stock levels
Inventory Replenishment Models
Min/Max Inventory Replenishment:
This model triggers restocking when a product reaches a minimum threshold, ideal for SKUs with predictable and seasonal demand. While it minimizes ordering costs, it often results in high carrying costs and requires more storage space.
Demand Inventory Replenishment:
Suitable for warehouses with limited space, this model replenishes stock just enough to fulfill pending orders without leaving excess inventory, optimizing space usage.
Top-Off Inventory Replenishment:
This model uses min/max thresholds and operates on a set schedule, replenishing stock in picking areas based on projected demand or staffing levels. It's effective during less active picking times or staff shortages, promoting efficient interleaving in busy areas.
Periodic Inventory Replenishment:
Inventory is moved to picking locations at set intervals based on demand forecasts, with stock levels reviewed at the end of each interval. This model suits large storage areas, with lower carrying costs but higher ordering costs due to larger volume movements.[15]
Monitoring and Tracking
Monitoring and tracking involve real-time oversight of inventory and warehouse operations. These functions ensure accurate visibility of stock levels, locations, and movement within the warehouse, allowing for efficient management and quick response to changes in demand. By using barcodes, RFID tags, and other tracking technologies, WMS provides detailed data on the status and history of each item. This capability helps prevent stockouts, overstocking, and misplacement of goods. Furthermore, it enhances transparency and accountability, leading to improved overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance relies on analytics rather than scheduling within a warehouse management system. These analytics are designed to foresee potential issues or errors before they occur. The primary advantage of predictive maintenance is that it only performs maintenance when necessary, thus eliminating unnecessary WMS downtime. Additionally, it can predict faults in real-time before they happen, further reducing downtime. By analyzing historical patterns of inaccuracies within the WMS, predictive maintenance analytics can predict and address faults before they arise. Before performing maintenance, the system sends notifications or alerts to the relevant department, facilitating easier execution of maintenance tasks.[16]
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting involves predicting future customer demand to optimize inventory levels and warehouse operations. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and seasonal patterns, WMS can generate accurate forecasts that help businesses ensure they have the right products in the right quantities. This predictive capability minimizes the risk of stockouts and overstocking, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced carrying costs. Advanced WMS solutions integrate machine learning algorithms to continually refine and enhance forecast accuracy. Additionally, demand forecasting aids in better workforce planning and resource allocation. Overall, it enables more efficient and responsive supply chain management, aligning inventory with actual market demand.[17]
Throughput Analysis
Throughput analysis involves evaluating the efficiency and performance of warehouse operations, particularly focusing on the movement of goods through the warehouse. This analysis examines key metrics such as the time taken to process orders, the flow of materials, and the utilization of warehouse resources. By understanding these factors, businesses can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that hinder productivity. Throughput analysis often employs both analytical and simulation models to predict system behavior under various scenarios. It helps in optimizing order picking systems, reducing congestion, and improving overall throughput. Effective throughput analysis ensures that warehouses operate at maximum efficiency, meeting customer demands promptly and reducing operational costs.[18]
Capacity Planning
Warehouse capacity planning involves managing the inventory stored in a warehouse. Given the constant movement of inventory in and out, it is vital to ensure the right amount of stock is available to meet customer demand while maintaining enough space to efficiently receive and distribute goods. Simultaneously, it is important to avoid unsold inventory occupying valuable space.
To accomplish these objectives, it is necessary to calculate warehouse space utilization. By understanding the principles of warehouse capacity planning and space utilization, warehouse operations can be optimized, thereby enhancing overall efficiency.[19]
Cycle Counting
Cycle counting is the periodic process of counting warehouse inventory to ensure accuracy and up-to-date records. This practice helps prevent stockouts, overages, and related shipping and warehousing errors. Conducting cycle counts allows companies to verify that physical inventory SKU counts match their WMS records. When integrated with an ERP, it also balances the ERP 'four-walls' inventory against the WMS location inventory. This technique involves routine physical counts and necessary adjustments for specific SKUs, ensuring that all inventory is counted over time.
Warehouse and supply chain managers typically create a plan for their staff to audit the inventory regularly. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers often need to count their client’s inventory on a scheduled basis. To do this efficiently, a system must be in place to record inventory levels while staff perform their normal duties. Manual or paper-based warehouses face more challenges with cycle counting due to the need to suspend inventory activities for accurate counts. In contrast, real-time, non-paper-based WMS allows operations to continue without interruption, significantly reducing the cost of cycle counting as normal business can proceed uninterrupted.[20]
Pick and Pack Optimization
Pick and pack optimization is a warehouse management strategy aimed at enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of order fulfillment. It involves organizing warehouse layouts to reduce travel time for pickers, employing advanced picking methods such as batch picking or zone picking, and utilizing technology like barcode scanning to minimize human error. Streamlining the picking process also boosts customer satisfaction, thereby fostering greater customer loyalty.[21]
Cost Analysis
Cost analysis involves evaluating all costs associated with warehouse operations to identify areas for efficiency improvements and cost savings. This process includes examining direct costs such as labor, storage, and equipment, as well as indirect costs like utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. By analyzing these costs, businesses can determine the total cost of ownership (TCO) for their warehouse operations.
Key metrics often reviewed in cost analysis include the cost per unit handled, cost per order processed, and cost per square foot of warehouse space utilized. The goal is to pinpoint inefficiencies and develop strategies to optimize resource allocation, streamline processes, and reduce overall expenses. Effective cost analysis also involves comparing current costs against industry benchmarks and historical data to gauge performance.
Additionally, integrating cost analysis with advanced WMS functionalities, such as real-time data tracking and automation, enhances accuracy and decision-making. This integration allows for more precise forecasting, better inventory management, and improved supplier negotiations, ultimately leading to a more cost-effective and efficient warehouse operation.
Conclusion
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are essential tools for modern logistics and supply chain management. They provide comprehensive solutions for inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and warehouse optimization. By automating key processes and integrating with other enterprise systems, WMS helps businesses reduce errors, lower costs, and enhance efficiency. The real-time data and analytics capabilities of WMS enable better decision-making and improved responsiveness to market demands. The integration of data analytics and AI further enhances WMS by enabling predictive maintenance, optimizing inventory levels, and providing valuable insights into operational performance. As supply chains become more complex and customer expectations rise, the adoption of WMS ensures that businesses can maintain high levels of operational performance, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage.
References
- [0] Why you still need WMS when you have already used ERP?
- [1] What Is A Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
- [1] What is Warehouse Management System (WMS)? [E-commerce Glossary]
- [2] What Is Warehousing? Definition, Functions and Advantages
- [2] What is Warehousing? Definition, Advantages, and Functions Explained
- [3] What is WMS (Warehouse Management System)?
- [3] What is a warehouse management system (WMS)? | Definition from Tech...
- [3] What Is A Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
- [4] 16 Key features of warehouse management systems (WMS) - Blog DeSmart
- [5] Investigation Into Popular WMS Software - Technical Articles
- [6] Supply Chain Logistics Software | Blue Yonder
- [7] SAP® Extended Warehouse Management 2020 Development Overview, Part 2 – Enhanced Integration
- [8] Oracle® Warehouse Management Implementation Guide
- [9] Supply Chain Management | Microsoft Dynamics 365
- [10] Infor SCM WMS Software - WMS Pricing, Demo & Comparison Tool
- [11] Softeon Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- [13] LEA Reply™ Warehouse Management
- [14] Inventory Planning Guide: Methods, Solutions & Steps